Home page
» GEOGRAPHY
» Physical Geography
» Physical geographical division
Physical geographical division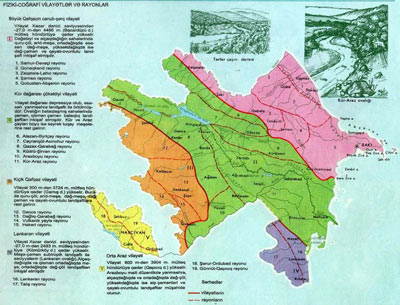 The landscape complexes are available in the territory of the republic in accordance with various forms of relief. Therefore, there are different physical-geographical regions. Greater Caucasus, Lesser Caucasus, the Kura-Araz and Lankaran and the Middle Araz are physical-geographical regions in the country. They are sometimes called as natural regions.
At division of Azerbaijan in the physical and geographical regions the common nature of geomorphological structures and landscape elements of the regions are taken as the main factor into consideration. On their basis the Front Asia with the Caucasus, Small Caucasus, Lankaran and Orta Araz (Nakhichevan) physical-geographical regions, and this also includes the Greater Caucasus and the Kura-Araz physical-geographical regions. In turn they are divided in 5 physical-geographical areas and 19 physical-geographical regions.
I. Physical-geographical region of the Greater Caucasus.
1. Samur –Devechi region,
2. Gonagkend region,
4. Mountainous Shirvan (Shamakhi) region,
5. Gobustan-Absheron region
II. Physical-geographical region of the Kur River lowland.
2. Alazan-Ayrichay region,
3. Gazakh-Garabagh region,
4. Kudru-Shirvan region,
6. Central Aran region
III. Physical-geographical region of the Lesser Caucasus.
1. Ganja Mountains region,
2. Mountain region of Nagorno-Garabagh,
3. Garabagh volcanic highland region,
4. Hakari region
IV. Physical-geographical region of Lankaran.
1. Lankaran region,
2. Talish Mountains region
V. Middle Araz (Nakhchivan) physical-geographical area.
1. Sharur-Ordubad region,
2. Nakhchivan Mountains (Gunnut-Qapıcıq) region
Physical-geographical region of the Great Caucasus
The Great Caucasus Mountains cover the north and north-eastern parts of the republic. Within the region the following physical-geographical regions are available:
Samur-Devechi physical-geographical region.
Physical-geographical region located in the north-east of the Great Caucasus is consistent with the Samur-Devechi lowland. It is covered in the east with the Caspian Sea, in the north with Samur River. Areas in the south up to mouth of the Gilgilchay and in the west up to 200 meter height included in region. The shores of sea descends for 26 m. from ocean level and covered with marine sediments. There are a lot of river sediments and cones in the West. Shollar plain is located between the Samur and Gudyal rivers.
Samur-Devechi region included in dry semi-desert climate zone with mild winters. About 300-400 mm of precipitation falls per year. The area of Samur-Devechi region become fully assimilated and turned to sown areas .
Gonagkend physical-geographical region.
Physical-geographical region covers the area from the watershed of the Greater Caucasus mountains up to Samur-Devechi lowland areas. In mountains from down to up in the south-east the mild-warm climate with dry summer and mild-warm climate with dry winter, mild-warm climate with equally distributed precipitations in the north-east, cold climate with dry winter and mountain-tundra climate replace each other. In this regard, the amount of precipitation is 400 mm to 1200 mm.
Zagatala-Lahij physical-geographical region.
The area is located on the southern slopes of the Caucasus Mountains. Physical-geographical region stretches in the west from Mazimchay to the east up to the Girdiman river. In the south its borders pass through Alazan-Eyrichay Valley, in the northfrom Watershed ridges (the Caucasus Mountains). The relief within this areas increases from 600 m to 4000 m.
Shamakhi (Shirvan) physical-geographical region.
The south-eastern edges of the Greater Caucasus Mountains included in the region. The region stretches in the north of the Caucasus ridge from watershed up to Shirvan plain in the south and south-west. Mountainous Shirvan covers the area from Qobustan in the east to Girdiman river in the west.
Mountainous Shirvan region has dry summers and warm-temperate climate. 400-900 mm of precipitation falls during the year.
Gobustan-Absheron physical-geographical region.
Gobustan-Absheron area located in the eastern part of the Greater Caucasus covers the area from the coasts of the Caspian Sea to Gadi mountain in the north-west (1222 m). The region stretches in south-west to Shirvan plain, in south to South-east Shirvan plain. The mild winters with dry climate and dry steppe climate predominate here. As the south-east edges of the Gobustan stay away from wind influence, so it is the area with less precipitation (150 mm).
In gray-brown and gray-brown soils of Gobustan-Absheron wormwood, saline, camel grass and eephemeris grow. They include in semi-desert landscape zone and covers an area as a whole. Chestnut soils prevail in the eastern part of the region. There are sandy areas on the shores of the Caspian Sea.
Physical-geographical region of the Kur-River lowland
It occupies ⅓ part of the territory of Azerbaijan. It stretches from Garayazy to to the Caspian Sea. The area is divided into the following physical-geographical regions:
Jeyranchol-Ajinohur-physical-geographical region.
Area along the left banks of the Kura River, from borders of Georgia to Girdiman River is occupied by Ajinohur-Jeyranchol region. This region is located between the Great Caucasus Mountains in the north and the Kura-Avaz lowland in the south.
Jeyranchol-Ajinohur is located in the semi-desert and dry steppe climate with mild winter and the north-eastern part in the mild warm climate. Annual amount of precipitation in the area is 300-400 mm. Jeyranchol in winter and Ajinohur in summer is dry.
The wormwoods,i semi-desert vegetation, white grass, lame, small bushes of mountain xerophytic vegetation are wide-spread here. Eldar pine forests, juniper, gum tree are the main elements of the local flora.
Alazan-Ayrichay physical-geographical region.
The physical-geographical region located in the valley of the same name. Its borders in the north consist of the south foothills of the Caucasus Mountains, low mountains of Ajinohur in the south, Mazun river in the west and Girdiman river in the east.
EThe climate of the area is mild-warm with dry winter and annual precipitation of 400-600 mm to 1000 mm.
In the Alazan-Ayrichay valley meadow-forest and meadowsoils were formed. Due to closeness of groundwater to the surface the oak, hornbeam, poplar and alder forests are available here. In the southern areas, in topper areas various grassy steppe vegetation can be found.
Physical-geographical region of the Gazakh-Garabakh.
Together with Ganja-Gazakh and Naftalan inclined plains the part of Garayazi, Garabagh and Garabakh and Mil plains are included in Gazakh –Garabagh region. These areas join the natural area of Lesser Caucasus in the south and west,where from its height m increases up to 400.
Kudru- Shirvan physical-geographical region
The region stretches from the Turyan River in the west to the foothills of the chain of Langabiz to the east. Its northern borders pass on line that connects the cities of Agdash-Goychay-Agstafa, and the southern borders on the cities of Agdash-Ujar-Kurdamir-Shirvan.
Kudru-Shirvan has a mild winter, and is located at dry, semi-desert and dry steppe climate zone. In the north, at a small area mild-warm climate in the dry winter dominates. Annual precipitation is 300-400 mm.
Physical-geographical region of sloping plains around the Araz.
Physical-geographical region is located between the Lesser Caucasus Mountains and Araz River. It covers a wide area from Zangilan region to Garabakh canal. Sloping plains along the Araz river included in areas along the Araz River. It is divided into Gayan, Inja and Harami steppes.
Areas are located at semi-desert and arid climate zones. Its annual precipitation is 400-600 mm.
Physical-geographical region of the Central Aran.
Areas in the central and eastern p
arts of the Kura-Araz lowland, countered with 0 m of height included in the Central Aran region.
In Central Aran semi-desert and dry steppe climate with mild winters predominates. The average annual temperature here rises above 14.5 °C. Absolute minimum temperature is -22 °C, and the absolute maximum temperature is 43°C. Although the amount of precipitation decreases towards the west, but least rainfall is observed in South-East Shirvan.
Tugay forests grow in aluvial-meadow soils along the Kura River. There are gum trees to the south-east of Barda in Sultanbud forests. Semi-desert landscape formed in the plains of republic mostly comes on the Central Aran physiographic region.
Physical-geographical region of the Lesser Caucasus
It mainly covers the Lesser Caucasus Mountains. Lesser Caucasus is divided into the following physical-geographical regions:
Physical-geographical region of the Ganja mountains.
Ganja mountains region stretches to Tartar River valley in the east. Northern borders of the region passes over line that unites cities Gazakh-Tovuz- Shamkir-Goranboy-Tartar.
At low and mid mountainous areas of physical-geographical region the temperate climate with dry winters, the cold high-mountain climate with dry winter predominates. The upper parts of Murovdagh range is located at mountain- tundra climate conditions. Annually 400-900 mm of precipitation falls here.
Slopes of the mountains are covered with brown, mountain, forest-mountain and mountain-meadow soils. Mountain bushes, forests, mountain meadows are developed in these areas. In Ganja mountain physical-geographical region mountain steppes, mountain forests, alpine meadows, rocky alpine meadows and rocky landscape zones are formed.
Physical-geographical region of Garabakh mountains.
Areas of location of Garabagh region are compatible with the same name. It is surrounded by Mudovdag range in the north, Garabagh and Mil plains to the east. The border along the watershed of Garabagh ridge passes at south-west.
In south-eastern edges of the region dry summers and warm-temperate climate, dry winter with warm-temperate climate zones formed in the foothills. At high mountain areas the cold winter climate with dry climate predominates. By increased of altitude the precipitation varies between 600-1000 mm.
Physical-geographical region of the Karabakh volcanic plateau.
Its western side passes at the border with Armenia, and eastern part over Garabakh watershed. The volcanic plateau is located at zone with cold dry climate in winter. Mountain-tundra climate predominates in areas of high mountains. The amount of precipitation varies from 600 mm to 900 mm. In connection with higher absolute altitude of the region the specific soil and vegetation cover are formed at high mountainous areas.
Hakari economic-geographical region.
Hakari physical-geographical region located along the Hakari and Okhchu rivers stretches along the state borders with Armenia in the west and with Iran to the south.
Warm-temperate climate with dry winter, semi-desert and dry steppe climate along the Araz River are the main climate types here. Amount of precipitation varies from 300 to 600 mm. The wormwoods, bushes and ephemeries are main plants here
Physical-geographical area of Lankaran
The south-east edges of Azerbaijan included in Lankaran physical-geographical area. The area is covered with the Caspian Sea in the east, with Iran in south and west.
In accordance with the mountainous and plain relief forms Lankaran area is divided in two physical-geographical regions.
Lankaran physical-geographical region
Lankaran region is located between the Talysh mountains and the Caspian Sea. These areas are consistent with the Lankaran lowland. Its northern borders pass along the Bolgar River, and the southern borders on Astara river. The absolute height of the physical-geographical region rises up to 40-50 meters.
The humid sub-tropical climate prevails in Lankaran.
Talysh mountains physical-geographical region
The ridges of Talysh mountains are related to the same name territory of the physical-geographical region. The region stretches up to our borders with Iran in the south and west.
In the eastern part of the physical-geographical region, at low mountainous areas the precipitations throughout the year distribute equally and the temperature are mild-warm, and the dry summers with warm-temperate climate prevail in the west.
Middle Araz (Nakhchivan) physical-geographical region
Physical-geographical region of Nakhchivan covers Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The region is divided into two physical-geographical regions:
Sharur-Ordubad physical-geographical region.
The sloping plains stretched along the left bank of the Araz River included in Sharur-Ordubad region.
The semi-desert and dry steppe climate with cold winter predominates on the plains. Throughout the year, the absolute minimum of air temperature is -32 ° C, and the absolute maximum temperature is 43 ° C.
Nakhchivan Mountains (Gunnut-Qapıcıq) physical-geographical region.
In Autonomous Republic the mountains rising from 1200 m up to the Gapijiq top are related to mountain region of Nakhchevan. Nakhchevan Mountains are located at dry summer cold climate zone. The precipitation in low mountainous areas amount to 300 mm, in mid mountainous areas - 400-600 mm, in high mountain areas - 800-900 mm.
|
